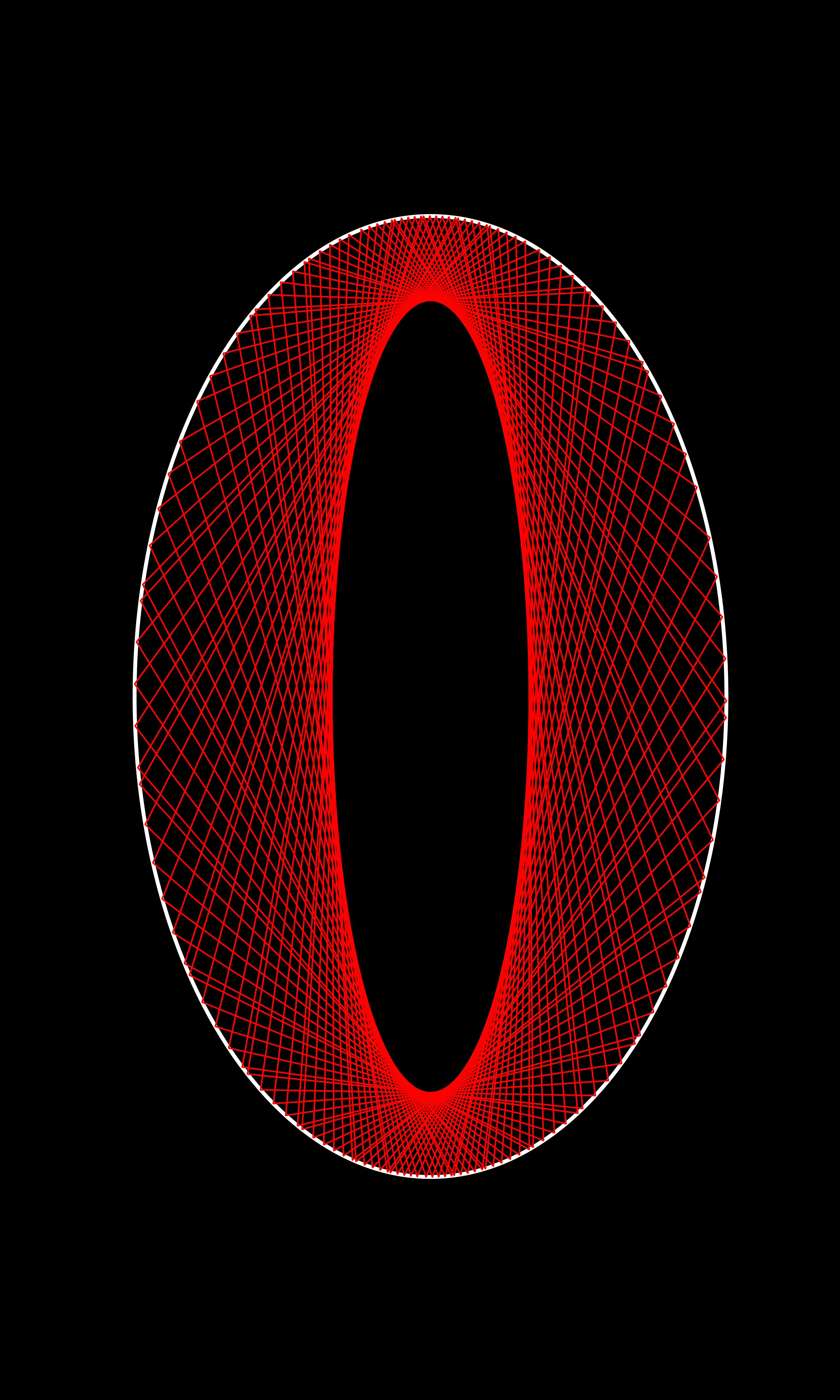
this article is to record how I create a image when a ball bounces insides a bigger ellipse,can copy the below code to get a image directly. but this post doesn’t take care the overlap, so it won’t be the best accurate.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def solve_quadratic_equation(a, b, c):
delta = b**2 - 4 * a * c
if delta > 0:
x1 = (-b + (delta**0.5)) / (2 * a)
x2 = (-b - (delta**0.5)) / (2 * a)
return x1, x2
elif delta == 0:
x1 = (-b + (delta**0.5)) / (2 * a)
return x1, x1
else:
return False
# Define the curve function
def curve(x, xt, yt): ##to get y on the track
return np.sqrt(yt * yt * (1 - (x**2) / (xt * xt)))
def curve_y(y, xt, yt):
return np.sqrt(xt * xt * (1 - (y**2) / (yt * yt)))
def tangent_slope(x, y, xt, yt):
m = -(yt * yt * x) / (xt * xt * y)
return np.array([1, m])
def normal_slope(x, y, xt, yt):
mn = (xt * xt * y) / (yt * yt * x)
return np.array([1, mn])
def get_incident_point(oldPosition, newPosition, xt, yt):
x = -100
y = -100
vector = np.subtract(newPosition, oldPosition)
xRange = [min(oldPosition[0], newPosition[0]), max(oldPosition[0], newPosition[0])]
yRange = [min(oldPosition[1], newPosition[1]), max(oldPosition[1], newPosition[1])]
if xRange[0] == xRange[1]:
x = xRange[0]
tmpY = curve(x, xt, yt) ###>0
if tmpY >= yRange[0] and tmpY <= yRange[1]: ##make sure it is in the range.
y = tmpY
else:
y = -tmpY
return (x, y)
if yRange[0] == yRange[1]:
y = yRange[0]
tmpX = curve_y(y, xt, yt)
if tmpX >= xRange[0] and tmpX <= xRange[1]:
x = tmpX
else:
x = -tmpX
return (x, y)
"""
A = a*a*k*k + b*b
B = 2*a*a*k*t
C = a*a*t*t - a*a*b*b
"""
###y = kx + t
k = round(vector[1] / vector[0], 6)
t = oldPosition[1] - (k * oldPosition[0])
### x**2 -kx -b- 3 = 0
a = xt * xt * k * k + yt * yt
b = 2 * xt * xt * k * t
c = xt * xt * t * t - xt * xt * yt * yt
delta = b**2 - 4 * a * c
if delta >= 0:
x1, x2 = solve_quadratic_equation(a, b, c)
# print("k=",k, "b=",b, "t=",t, "delta=",delta,"x y =", (x1,y1), (x2,y2))
point_ = [[x1, x1 * k + t], [x2, x2 * k + t]]
if round(np.linalg.norm(np.subtract(oldPosition, point_[0])), 12) <= round(
np.linalg.norm(np.subtract(oldPosition, point_[1])), 12
):
x = point_[0][0]
y = point_[0][1]
else:
x = point_[1][0]
y = point_[1][1]
else:
print("something wrong, didn't get the incident point")
return False
return (x, y)
def normalize(v):
norm = np.linalg.norm(v)
if norm == 0:
return v
return v / norm
xt = 3
yt = 5
rayPoints = [[[1, 0]]] ###would be many rays
rayVector = [[0, -0.3]] ###would be many vectors
indexFrame = 1
totalFrame = 3200
index = 0
C = np.sqrt(yt * yt - xt * xt) ####2*yt
f1 = [0, C]
f2 = [0, -C]
collisions = []
while True:
currentPoint = rayPoints[index][-1]
nextPoint = np.add(currentPoint, rayVector[index])
# print(nextPoint)
nextPointX = round(nextPoint[0], 12)
nextPointY = round(nextPoint[1], 12)
flag = True
distance = np.linalg.norm(np.subtract(nextPoint, f1)) + np.linalg.norm(
np.subtract(nextPoint, f2)
)
if distance >= 2 * yt:
flag = False
if indexFrame > totalFrame:
break
indexFrame = indexFrame + 1
# print(round(nextPointY,6), curve(nextPointX),">>", gap)
if flag: ## keep vector, and add one point
rayPoints[index].append(nextPoint)
collisions.append(0)
# print("passed", nextPoint, currentPoint, curvePoint)
else: ##need to change vector and add one point
x, y = get_incident_point(nextPoint, currentPoint, xt, yt)
curvePoint = [x, y]
collisions.append(1)
# print("down to curve", indexFrame,distance, nextPoint, currentPoint, curvePoint)
normal_vector = normal_slope(x, y, xt, yt)
normal_vector = normalize(normal_vector)
# print(">>>>>",x, round(x,5), normal_vector, rayVector[index])
rayVector[index] = (
rayVector[index]
- 2 * np.dot(rayVector[index], normal_vector) * normal_vector
)
# print(">>>>>",x, round(x,5), normal_vector, rayVector[index])
rayPoints[index].append([x, y])
# print(rayPoints)
xRay = []
yRay = []
for x in rayPoints[index]:
xRay.append(x[0])
yRay.append(x[1])
theta = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 10000)
xRange = xt * np.cos(theta)
yRange = yt * np.sin(theta)
##y = x**2 - 3, k = 2x
viewRangeX = [-4.5, 4.5]
viewRangeY = [-4.5, 4.5]
plt.style.use("dark_background")
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=[xt, yt])
# ax.set_xlim(viewRangeX[0], viewRangeX[1])
# ax.set_ylim(viewRangeY[0], viewRangeY[1])
plt.axis("off")
ax.plot(xRange, yRange, linewidth=1, color="w")
ax.plot(xRay, yRay, "-", linewidth=0.4, color="r", markersize=2)
ax.plot([xRay[-1]], [yRay[-1]], "-", linewidth=2, color="r")
plt.savefig("imgae12.png", dpi=1000)
# plt.show()